AI for Nonprofits: How the New Google AI Experience Will Impact Search Results

Request a Demo
Learn how top nonprofits use Classy to power their fundraising.
In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, search engine optimization (SEO) has long been the cornerstone of successful online visibility. Google, the dominant player in the search engine realm, has consistently introduced updates to its algorithms, shaping how it ranks and discovers websites.
Now, imagine a future where artificial intelligence (AI) takes center stage, revolutionizing the organic search landscape as we know it. With the introduction of Google’s groundbreaking new AI experience, the impact on organic search is nothing short of transformative.
In this blog post, we dive into the possibilities ahead, exploring how Google’s AI advancements will influence website rankings, user behavior, and the future of SEO strategies. Get ready to unlock the doors to a new era of organic search.
Google AI 101: Understanding the Basics
At its core, Google’s new AI experience leverages advanced machine learning algorithms and natural language processing capabilities to understand the intent and context of each query. It goes beyond keyword matching, aiming to provide users with more relevant and tailored search results.
This development marks a paradigm shift in how Google discovers websites and ranks them in organic search results—websites that align more closely with the user’s intent and offer high-quality content will likely gain visibility. Catering to the user’s needs is now just as critical as optimizing for particular keywords.
This means website owners and digital marketers like yourselves must adapt their SEO strategies to align with these new AI-driven algorithms to stay competitive in the ever-evolving online landscape.
So how do you do that? Let’s first dive into the AI experiences currently available to the public or offered in beta to understand what Google users can expect in the coming months.
Google Bard
There are currently two components of Google Bard: the standalone AI experience and the generative AI search experience.
Introducing Bard
Google Bard is a large language model (LLM) chatbot developed by Google AI. It’s an advanced technology that uses machine learning to generate human-like responses based on the provided prompts.
Bard’s standalone AI experience is still under development but already capable of things like:
- Translating languages for easy comprehension
- Answering detailed prompts in a clear, concise way
- Generating creative content like blog posts, poems, code, musical pieces, and more
- Working with other Google apps to help accomplish tasks more efficiently
Introducing the Bard AI Search Experience
Google Bard’s AI search experience offers a new way to search the web. It uses generative AI to understand the nuances of people’s queries better, leading to more precise results.

When you search for something on Google Bard, you’ll see results like:
- AI-powered snapshots of short, human-like summaries that provide a tailored response to users’ queries
- AI-powered answers consisting of longer, more detailed responses to more complex concepts
- Traditional search results that you’re used to seeing on Google, but now supplemented with the AI-powered snapshots and answers introduced above
Creating high-quality, relevant, and engaging content that satisfies user intent is more important than ever. Additionally, understanding how to optimize content for AI-driven search algorithms will play a crucial role in improving organic search rankings and driving traffic to your websites.
While that answer is still unclear, we’ll update this blog as we test the beta experience and identify the most effective strategies.
What to Expect With Google Bard’s AI Search Experience
So far, we see a few notable features:
- Bard will answer commercial and informational queries
- Bard will not answer “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) queries
- Bard users can view the sources referenced to craft its summary within the AI snippet box
- Bard users can expand the AI snippet box and see corroborated information in a line-by-line breakdown
When an AI response appears in search results, it pushes search engine results page (SERP) features, like featured snippets, images, videos, People Also Ask, knowledge panels, and organic search results, below the fold. This is significant because it confirms that the new Google AI experience heavily favors AI-generated results.
Google Perspectives
Like the motivation behind Google Bard, Google Perspectives leverages generative AI to help users navigate more effectively and discover the information they seek more easily.
Google Perspectives factors in the importance of what others have to say on a particular topic and feeds users long- and short-form videos, images, and written posts that people have shared on discussion boards, Q&A websites, and social media platforms relating to certain queries.
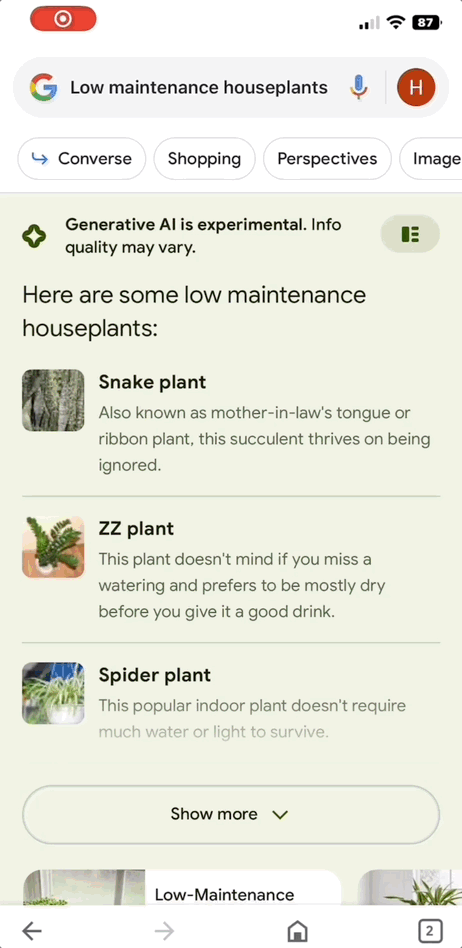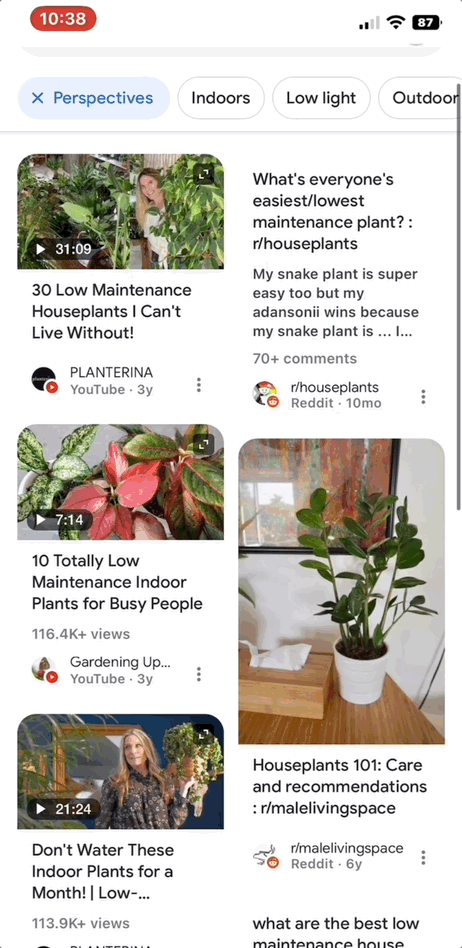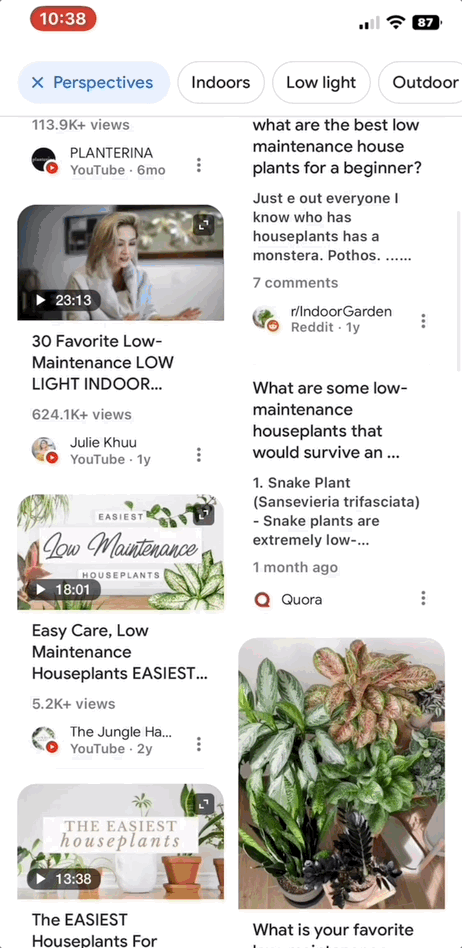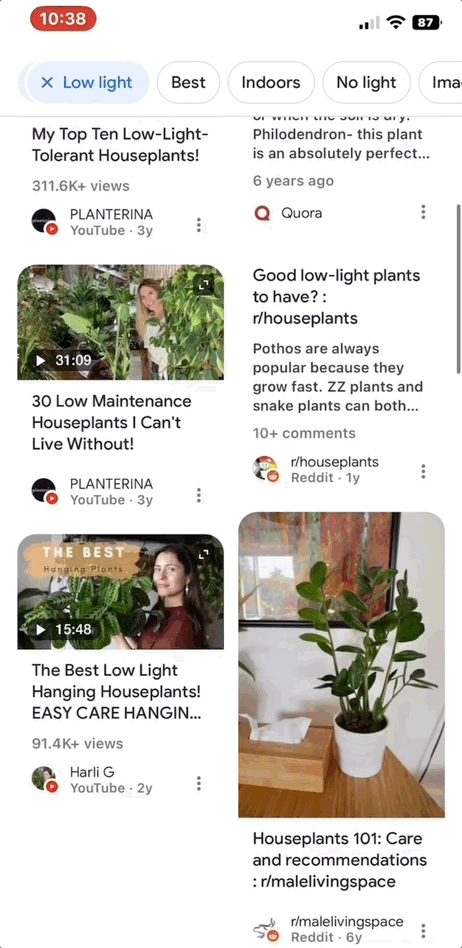
Generally, Google Perspectives appears in search when users may benefit from the advice or personal feedback of others regarding their query. For example, if you searched “Low maintenance houseplants” and tap the Perspectives filter, you’ll see a page of results with advice from other people, like personal stories told through videos or tips from commenters on Reddit.
What to Expect With Google Perspectives
In its current functionality, we see:
- Google’s content ranking will show more “hidden gems” (comments in a thread, posts on an emerging blog, geo-tagged Instagram photos, etc.) through its Perspectives tool to source information that lives in hard-to-reach places
- Google shares details about the creators of this featured content as well, such as their names and profile photos
Google’s Perspectives tool offers snackable content that exposes users to simplified, vetted responses to particular queries. Just like people seek advice from friends and family, they can now go directly online to seek trusted responses from real people who have advice, opinions, and experiences to share.
How to Proceed in the Age of AI
With all these changes, you may be thinking, or potentially might have heard, that “SEO is dead.” But in reality, SEO remains critical to a strong digital strategy, and companies that continue evolving and investing in SEO efforts will likely find success in the future.
Let’s dive into three ways your nonprofit can continue strengthening its digital performance in response to Google’s new AI search experience.
1. Join the Google Labs Waitlist
Google Bard, the standalone AI experience, is now accessible to all, but its generative AI search experience is still under development. To access the search experience and engage with the technology in beta, we highly recommend joining the Google Labs waitlist.
Beta-testing functionality comes on a first-come-first-served basis, meaning those who requested access to the experiment when the option first became available are those who were initially approved and are currently exploring the experiment.
The waitlist to join Google Labs is still open, so the general public can experience it themselves once approved. Immersing yourself in the technology is the quickest way to learn what it currently offers, how it functions, and how it’s changing the search landscape.
2. Lean Into Thought Leadership Content
Understanding how effective generative AI already is in creating short-form content based on specific prompts, it’s worth questioning how your nonprofit’s content will emerge through the AI noise to remain relevant online.
Organizations that provide timely, thought-provoking content with a deep level of expertise will likely not see as much of an impact on digital performance as those relying on top-of-funnel content intended solely to drive traffic.
Large language model chatbots, like ChatGPT, can now supply lower-effort content with incredible efficiency and relatively high levels of accuracy, so writers and marketers need to evolve. The goal now is to offer something readers can’t get from AI, which is genuine thought leadership content written by experts in the space.
3. Prioritize EEAT Guidelines
In the context of digital marketing, EEAT stands for experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Prescribed by Google’s search quality rating guidelines, these guidelines help human evaluators to assess search results.
While not direct ranking factors, these guidelines provide insights into the factors that Google considers critical for determining how to rank a website. And in the age of AI, content that adheres to Google’s EEAT guidelines will be rewarded for serving as a top-tier resource that’s trusted and informative.
Learning to Embrace the Future of AI for Nonprofits
When technology evolves as quickly as it has over the last decade, it’s normal to feel overwhelmed. The concept of AI seemed a distant reality for most, then quickly became a part of our daily lives. If you’re feeling that way, you’re not alone.
Although understandable to be hesitant about embracing change, whether due to fear or comfortability with your current strategies, nonprofits must start the learning process to stay on pace. Not only is this critical for your organization’s visibility, but it’s also necessary for safeguarding your mission and sustaining revenue despite this online evolution.
At Classy, we’re committed to real-time learning to share our experiences and recommendations with you. We’ve already begun conducting research on the topic of AI in the following articles and encourage you to revisit our blog as we update these existing pieces with new AI developments as the space continues to progress:
- 5 Ways to Leverage ChatGPT for Your Nonprofit Blog
- A Nonprofit’s Guide to Crafting the Perfect Prompt for Language AI Tools
- Ethical Guidelines for Nonprofits Using Language AI Tools
We look forward to learning together.
Copy Editor: Ayanna Julien

Dive Into the Latest Fundraising Data
Subscribe to the Classy Blog
Get the latest fundraising tips, trends, and ideas in your inbox.
Thank you for subscribing
You signed up for emails from Classy
Request a Demo
Learn how top nonprofits use Classy to power their fundraising.


